The Allure and The Danger: A Guide to Using Leverage Responsibly in Crypto Trading
Let’s be honest. You’ve seen the screenshots. The wild 1000% gains from a single trade. The stories of traders turning a few hundred dollars into a small fortune overnight. The common thread? Leverage. It’s the turbo-boost for your crypto trading engine, promising to amplify your wins to dizzying heights. But here’s the raw truth most people skip over: it’s also a direct-line ticket to ‘getting rekt’. Learning to use leverage responsibly in crypto isn’t just a good idea; it’s the only way to survive and potentially thrive in these volatile markets. It’s the difference between a calculated strategy and a trip to the casino.
Key Takeaways
- Leverage amplifies both profits and losses. A 10x leverage means a 10% market move against you can wipe out your entire position.
- Never risk more than 1-2% of your total trading capital on a single trade. This is the golden rule of risk management.
- Always use stop-loss orders. They are your non-negotiable safety net that automatically closes a losing trade at a predetermined price.
- Understand your liquidation price. This is the point where the exchange forcibly closes your position to prevent further losses, costing you your entire margin.
- Lower leverage (2x-5x) is far more sustainable for most traders than high leverage (20x-100x). Start small and build confidence.
So, What Exactly is Leverage in Crypto?
Forget the complicated financial jargon for a second. Think of leverage like a loan from the exchange. You put down a small amount of your own money, called margin, and the exchange lends you the rest to open a much larger position.
For example, if you want to buy $10,000 worth of Bitcoin but only have $1,000 in your account, you could use 10x leverage. You put up your $1,000 as margin, and the exchange ‘lends’ you the other $9,000. Now, you control a $10,000 position.
If Bitcoin’s price goes up by 5%, your $10,000 position is now worth $10,500. You close the trade, ‘repay’ the loan, and your initial $1,000 has grown to $1,500. A 50% profit from a 5% market move! That’s the magic. That’s the pull. But the dark side is just as powerful. If Bitcoin’s price drops by 5%, your position is now worth $9,500. That $500 loss comes directly from your margin, cutting your initial $1,000 in half. A 50% loss from a 5% move. It cuts both ways, and it cuts deep.

The Double-Edged Sword: The Highs and The Lows
It’s crucial to have a clear-eyed view of what you’re getting into. Leverage isn’t inherently good or bad; it’s a tool. And like any powerful tool, it can build or it can destroy.
The Pros (The Siren’s Call)
- Magnified Profits: This is the main attraction. Small price movements can lead to substantial gains, allowing you to grow a small account much faster than with spot trading alone.
- Capital Efficiency: You don’t need a massive amount of capital to control a significant position. This allows for diversification or for keeping most of your funds in cold storage while trading with a smaller portion.
- Shorting Opportunities: Leverage allows you to profit from a falling market. By ‘shorting’ an asset, you’re betting its price will go down. This is a vital strategy for hedging or profiting in a bear market.
The Cons (The Brutal Reality)
- Magnified Losses: The number one risk. The same multiplier that boosts your gains works just as fiercely on your losses. High leverage can obliterate your account with incredible speed.
- Liquidation Risk: This is the boogeyman of leverage trading. If the market moves against you by a certain percentage (determined by your leverage), the exchange will automatically close your position. You lose your entire margin for that trade. It’s a game over.
- Psychological Pressure: Watching your P&L swing by hundreds or thousands of dollars every few seconds is incredibly stressful. It can lead to emotional decision-making, like panic selling or revenge trading, which almost always ends badly.
- Funding Fees: Most exchanges charge fees for keeping a leveraged position open, known as funding rates. These can eat into your profits, especially if you hold a position for a long time.
Core Principles for Using Leverage Responsibly in Crypto
Okay, so you understand the risks but still want to proceed. Good. That awareness is the first step. Now, let’s build the framework that will keep you safe. Following these principles isn’t optional if you want to last in this game.
Start Small. No, Smaller Than That.
If you’re new to leverage, forget about 20x, 50x, or 100x. Just don’t. Start with 2x or 3x leverage. The goal here isn’t to get rich on your first trade; it’s to understand the mechanics and the emotional experience. How does it feel to see your position in the red? How quickly do small market moves affect your balance? Use a tiny amount of your capital—an amount you are genuinely okay with losing. Consider it the price of your education. Only after you’ve successfully managed trades at low leverage should you even think about inching it higher, and even then, most experienced traders rarely go above 10x.
Master Risk Management Like Your Life Depends On It
Because your trading life does. Risk management is the art of staying in the game long enough to be profitable. It’s your defense. Offense wins games, but defense wins championships.
The Golden Rule: Never, ever risk more than 1-2% of your *entire trading portfolio* on a single trade. If you have a $5,000 trading account, you should not be able to lose more than $50-$100 on any one trade if you are wrong.
How do you enforce this? Through two key concepts:
- Position Sizing: You don’t just ape into a trade. You calculate how much you can put into the trade based on your risk tolerance. The formula involves your account size, the percentage you’re willing to risk, and the distance to your stop-loss.
- Stop-Loss Orders: A stop-loss is an order you place with the exchange to automatically close your position if the price hits a certain level. It’s your escape hatch. It takes the emotion out of cutting a loss. A trade without a stop-loss is not a trade; it’s a gamble.
Think of it this way: You can be wrong on 7 out of 10 trades and still be a profitable trader if your winning trades are significantly larger than your losing trades. This is known as a good Risk-to-Reward (R:R) ratio. For example, you only enter trades where you can potentially make 3 times what you’re risking (a 1:3 R:R). This is only possible with disciplined risk management.
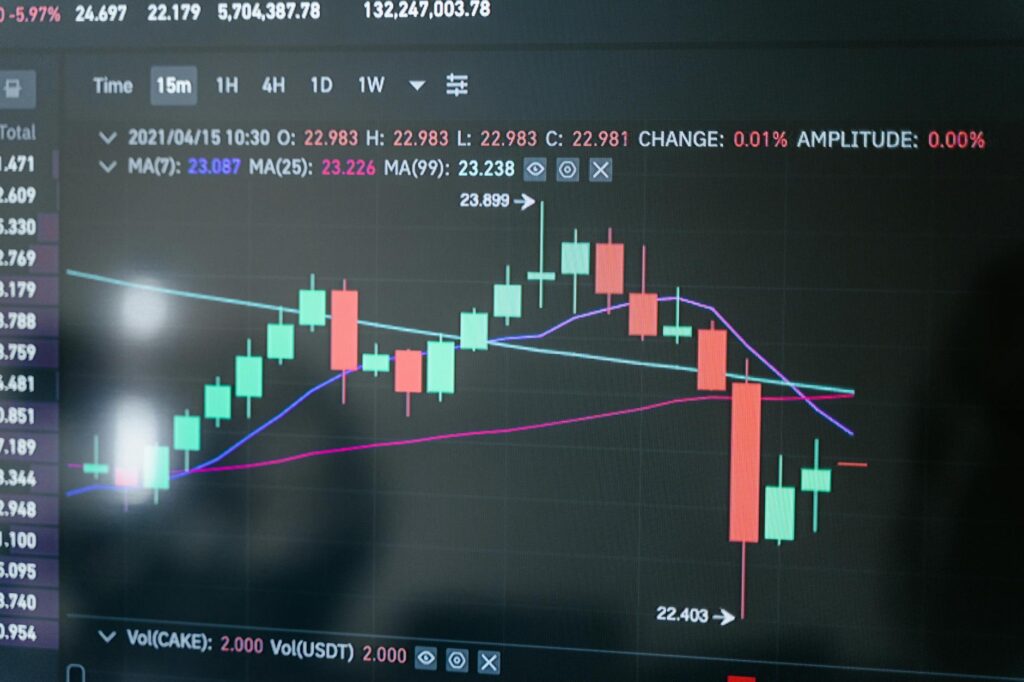
Understand Liquidation Price and Fear It
When you open a leveraged position, the exchange will show you a ‘Liquidation Price’. This is the price at which your losses become equal to your margin. If the asset’s price hits this level, the exchange’s systems will instantly and automatically close your position to ensure you don’t lose more money than you put in (and to protect the exchange’s loan). You lose everything you committed to that trade.
The higher your leverage, the closer your liquidation price is to your entry price. With 50x leverage, a mere 2% move against you can trigger liquidation. With 10x leverage, you have a bit more breathing room (around a 10% move). Your stop-loss should *always* be set well before your liquidation price. If your stop-loss gets hit, you lose your planned 1-2%. If your liquidation price gets hit, you lose the whole chunk of margin. It’s a catastrophic failure of risk management.
Never, Ever Go ‘All In’
This should be obvious, but the temptation is real. Never use your entire trading portfolio as margin for a single leveraged trade. It’s a surefire way to blow up your account. Crypto is infamous for its sudden, violent price swings—often called ‘scam wicks’—that can trigger liquidations in a flash before the price reverses. If you are all in, one of these wicks can end your trading career. Always trade with a small fraction of your capital and keep the rest safe.
Practical Steps and Essential Tools
Theory is great, but let’s get practical. How do you actually implement this stuff?
Setting Stop-Loss (SL) and Take-Profit (TP) Orders
This is your bread and butter. Before you even click the ‘buy/long’ or ‘sell/short’ button, you must know two things: where you’re getting out if you’re wrong (your stop-loss) and where you plan to take profits if you’re right (your take-profit).
- Stop-Loss (SL): Placed at a price level that would invalidate your trading idea. For example, if you’re buying Bitcoin because you believe it has found support at $60,000, you might place your stop-loss just below that level, say at $59,500.
- Take-Profit (TP): Placed at a price level where you want to secure your gains. This could be the next major resistance level on the chart. Having a TP helps you avoid getting greedy and watching a winning trade turn into a loser.
Almost every exchange interface will have clear fields for you to enter your SL and TP prices when you place an order. Use them. Every. Single. Time.
Calculating Your Position Size
This is where it all comes together. Let’s use our rule of risking 1% on a $5,000 account.
- Max Risk per Trade: $5,000 * 1% = $50. This is the most you can lose.
- Identify Your Trade Idea: Let’s say you want to long Ethereum at $3,500.
- Set Your Stop-Loss: You determine your stop-loss should be at $3,430.
- Calculate Risk per Unit: The distance from your entry to your stop is $3,500 – $3,430 = $70.
- Determine Position Size: Divide your max risk by the risk per unit. $50 / $70 = ~0.71 ETH.
So, your position size should be 0.71 ETH. It doesn’t matter if you use 2x, 5x, or 10x leverage to open this position; the amount you lose if your stop-loss is hit will still be $50. The leverage simply determines how much margin you need to post to open the position. Higher leverage means less margin required, but it doesn’t change the dollar amount you’re risking. This is a critical concept that separates professional traders from gamblers.
Choosing the Right Exchange
Not all exchanges are created equal. When trading with leverage, look for:
- High Liquidity: This means lots of buyers and sellers, which reduces the chance of ‘slippage’ (your order getting filled at a worse price than you wanted).
- A Stable Trading Engine: The last thing you want is for the exchange to crash or lag during high volatility.
- Fair Liquidation Mechanisms: Look for exchanges that use a ‘mark price’ based on an index of multiple spot exchanges, rather than just their own volatile last price, to determine liquidations. This can protect you from those ‘scam wicks’.
- Clear Fee Structure: Understand the funding rates and trading fees.
The Psychological War: Traps to Avoid
Leverage trading is as much a mental game as it is a technical one. Your biggest enemy is often yourself.
- Revenge Trading: You just took a loss. You’re angry. You immediately jump into another, larger trade to ‘win it back’. This is a recipe for disaster. If you get stopped out, step away from the screen. Take a walk. Clear your head.
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO): You see a coin pumping 20% and you jump in with high leverage at the top, fearing you’ll miss out on more gains. This often ends with you buying the peak right before a correction.
- Marrying Your Bags: You get into a position that immediately goes against you, but you’re so convinced you’re right that you move your stop-loss further down, refusing to accept the loss. This is how a small, manageable loss turns into a liquidation.
Conclusion
Using leverage in crypto trading is like handling fire. Used responsibly and with respect, it can be an incredibly powerful tool for warmth and progress. Used recklessly, it will burn you, and it will do it fast. The key to using leverage responsibly in crypto isn’t about finding a magic indicator or a secret strategy. It’s about discipline. It’s about having a rock-solid risk management plan and sticking to it no matter what. It’s about treating trading like a business, not a slot machine. Start small, respect the risk, manage your psychology, and you’ll give yourself a fighting chance to not only survive but potentially succeed where so many others have failed.



 Backtest Crypto Trading Strategies: A Complete Guide
Backtest Crypto Trading Strategies: A Complete Guide  NFT Standards: A Cross-Chain Guide for Creators & Collectors
NFT Standards: A Cross-Chain Guide for Creators & Collectors  Decentralized Storage: IPFS & Arweave Explained Simply
Decentralized Storage: IPFS & Arweave Explained Simply  How to Calculate Cryptocurrency Taxes: A Simple Guide
How to Calculate Cryptocurrency Taxes: A Simple Guide  Your Guide to Music NFTs & Top Platforms for 2024
Your Guide to Music NFTs & Top Platforms for 2024  TradingView for Crypto: The Ultimate Trader’s Guide
TradingView for Crypto: The Ultimate Trader’s Guide  Backtest Crypto Trading Strategies: A Complete Guide
Backtest Crypto Trading Strategies: A Complete Guide  NFT Standards: A Cross-Chain Guide for Creators & Collectors
NFT Standards: A Cross-Chain Guide for Creators & Collectors  Decentralized Storage: IPFS & Arweave Explained Simply
Decentralized Storage: IPFS & Arweave Explained Simply  How to Calculate Cryptocurrency Taxes: A Simple Guide
How to Calculate Cryptocurrency Taxes: A Simple Guide  Your Guide to Music NFTs & Top Platforms for 2024
Your Guide to Music NFTs & Top Platforms for 2024  TradingView for Crypto: The Ultimate Trader’s Guide
TradingView for Crypto: The Ultimate Trader’s Guide